Identify Three Kinds of Synovial Joints Giving Examples of Each
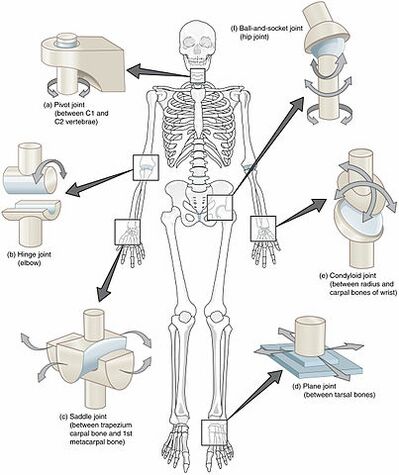
Synovial cartilaginous and fibrous. As shown on this illustration the six types of synovial joints include the pivot hinge saddle plane condyloid and ball-and-socket joints.
Synarthrotic amphiarthrodial and synovial.

. Try to use examples that include more than one type of. Gomphosis joints exist between teeth and the tooth sockets in your jaw. Examples of synovial joints include joints in the wrist elbow knees shoulders and hip.
Atlantoaxial joint radius e. An example of which would be the sutures joining the. Classify joints and specify each group according to function and structure.
-back and forth side to side. Objectives Describe the components of the axial versus appendicular skeleton. Which bones and joints are primarily involved in each activity.
Give an example of each 10. Types of Joints in the Human Body. Suture joints are present between the bones in your skull.
These joints are found in our shoulder joint neck joint knee joint wrist joint etc. The different types of synovial joints are the ball-and-socket joint shoulder joint hinge joint knee pivot joint atlantoaxial joint between C1 and C2 vertebrae of the neck condyloid joint radiocarpal joint of the wrist saddle joint first carpometacarpal joint between the trapezium carpal bone and the first metacarpal bone at the base of the thumb and plane joint facet. Radiocarpal joint of wrist c.
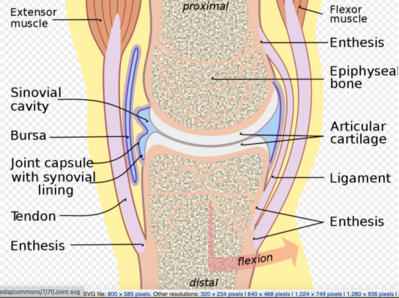
There is another connective tissue called tendon that attaches muscle to the bone at the joint. Synovial joints are flexible movable can slide over one another rotatable and so on. -variety of movements no rotation.
Tree types of synovial joint are. The three main types of joints are. Define the terms fibrous joints cartilaginous joints and synovial joints.
- fibrous connection is the short peridontal ligament. Name and describe the three types of fibrous joints. - teeth are embedded in their sockets.
Elbow and knee joint. Fibrous joints have fibrous tissue joining the bone and these joints are typically very strong. Also observe that the screen of the laptop or the door is movable but it only in a single plane.
Elbow knee intephallangeal joints d. -concave surface in one direction and convex in another. Ball and socket joint.
Answer01- 4 major classes of joints Ball-and-socket joints Hinge joints Pivot joints Ellipsoidal joints. Give an example of each. Thumb 1st metacarpal and trapezium.
The three types of fibrous joints are suture gomphosis and syndesmosis. These joints are found throughout the body. There are six types of synovial joints.
Name and define two types of cartilaginous joints. Planar hinge pivot condyloid saddle and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints. Describe the seven different.
Classify joints and specify each group according to function and structure. Ball and socket joint ex. Name and define three types of fibrous joints.
The synovial joints are the most common type of joint because this joint helps us to perform a wide range of motion such as walking running typing and more. See answer 1 Best Answer. Should Hip joint b.
So a type of synovial joint the hinge joint of our body also allows movement in a single plane and this is why we call it a hinge joint. Ball-and-socket condyloid gliding hinge pivot and saddle joints. However some locations serve as better examples than others.
There are six types of synovial joints. - is a peg-in-socket fibrous joint. Describe the five types of bones found in the human skeleton.
Define the terms fi brous joints cartilaginous joints and synovial joints. Three main structural components are found in all synovial joints and include a synovial cavity articular capsule and articular cartilage. Examples of hing joint.
Symphysis joints are permanent cartilaginous joints for example the pubic symphysis. There are three types of joints. Anatomically speaking joints are where two or more bones touch and they can be fixed or mobile.
Identify and describe different exercises or activities that involve using each of these joints. A joint is an articulation between two bones in the body and are broadly classified by the tissue which connects the bones. Give an example of each.
Fibrous cartilaginous and synovial. Examples are elbow joints ankle joints interphalangeal joints. - only example is the articulation of a tooth with its bony alveolar socket.
Different type of joints in the human body can be classified as planar hinge pivot condyloid saddle or ball-and-socket joints. Name and describe six classes of synovial joints and give an example of each. To begin our investigation lets focus on the pivot joints.
Synchondroses are temporary joints which are only present in children up until the end of puberty. The ball and socket is a type of synovial joint in which. For example the epiphyseal plates in long bones.
-oval-shaped condyle of one bone articulates with elliptical cavity of another. Ball-and-socket joints consist of a rounded ball-like end of one bone fitting into a cup-like socket of another bone. Fibrous joints also called synarthroses are the sturdiest joints in your body.
These joints do not allow movement to occur between the bones. Give an example of each. Planar Joints Planar joints have bones with articulating surfaces that are flat or slightly curved faces.
Between carpal bones of. Ball-and-socket joints- The ball and socket jointand it is also known spheroid joint. There are three categories of joints in the human body according to the National Library of Medicine NLM.
Identify the components of a synovial joint. Describe the three primary classifications of joints and give an anatomic example of each. The different types of synovial joints are the ball-and-socket joint shoulder joint hinge joint knee pivot joint atlantoaxial joint between C1 and C2 vertebrae of the neck condyloid joint radiocarpal joint of the wrist saddle joint first carpometacarpal joint between the trapezium carpal bone and the first metacarpal bone at the base of the thumb and plane joint facet.
A cartilaginous joint between two vertebrae. Name and Define three types of fi brous joints. Define the primary components found in bone.
Comments
Post a Comment